Syphilis: Treat It Early to Avoid Vital Complications
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) that can affect individuals at any stage of life, including teenagers. While the condition may cause embarrassment, early detection and treatment can lead to a complete cure. However, the best approach is prevention through measures like using condoms, avoiding multiple sexual partners, and carefully assessing the health of sexual partners. Regular STD testing is also critical. Despite these precautions, no method guarantees 100% protection against syphilis. Therefore, if there’s any risk of exposure, prompt testing and treatment are essential to avoid complications.
What Is Syphilis, and How Is It Transmitted?
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. Without timely treatment, it can spread through the body, causing severe complications such as nerve damage, organ failure, and even death. Understanding how syphilis is transmitted is key to preventing its spread.
How Is Syphilis Transmitted?
- Unprotected sexual activity: Transmission can occur through vaginal, anal, or oral sex, as the bacteria enter the body via small cuts or mucous membranes.
- Contact with syphilis sores: Direct contact with sores or lesions, typically found on the genitals, mouth, or hands, can spread the infection.
- Mother-to-child transmission: Pregnant women with syphilis can pass the infection to their baby during pregnancy or childbirth, leading to congenital syphilis.
- Contaminated needles or medical equipment: Using shared needles or improperly sterilized medical tools can also transmit the infection.
Who Is at Risk of Syphilis?
While syphilis is most commonly transmitted sexually, it can also be passed congenitally. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), more than 8 million people aged 15–40 were diagnosed with syphilis in 2022. High-risk groups include:
- Individuals with multiple sexual partners
- Those who do not use condoms
- People who have sexual contact with infected individuals
Syphilis Symptoms and Stages
Syphilis symptoms can be categorized into three main stages:
- Primary stage: Symptoms usually appear about 21 days after infection. Small, painless sores called chancres develop on the genitals, anus, or mouth. These sores typically heal on their own within 3–6 weeks.
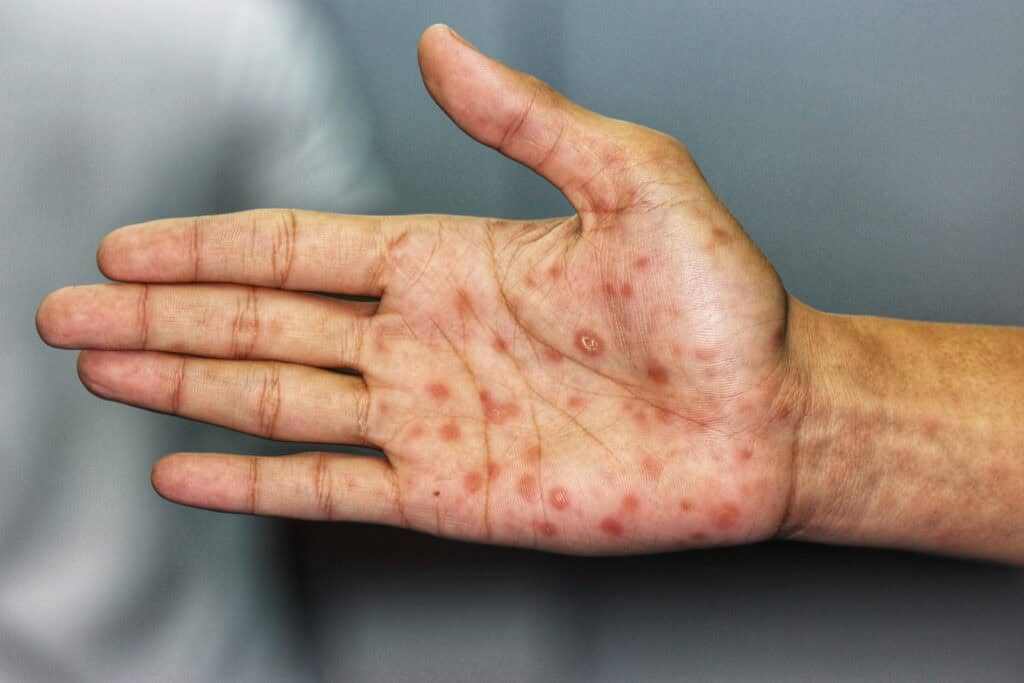
- Secondary stage: A rash may develop on the torso, palms, and soles, potentially spreading to other body parts. Other symptoms include fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes. If left untreated, the infection can progress to a latent stage with no visible symptoms.
- Latent stage: During this stage, there are no outward signs of the disease, but the infection remains in the body and can still be transmitted to others.
- Tertiary stage: If untreated, syphilis can reemerge in a severe form, damaging the nervous system, brain, heart, bones, and joints. This stage can be life-threatening.
Complications of Syphilis
- Increased risk of contracting HIV
- Blindness, hearing loss, or facial deformities
- Risk of stroke or paralysis
- Heart failure or death
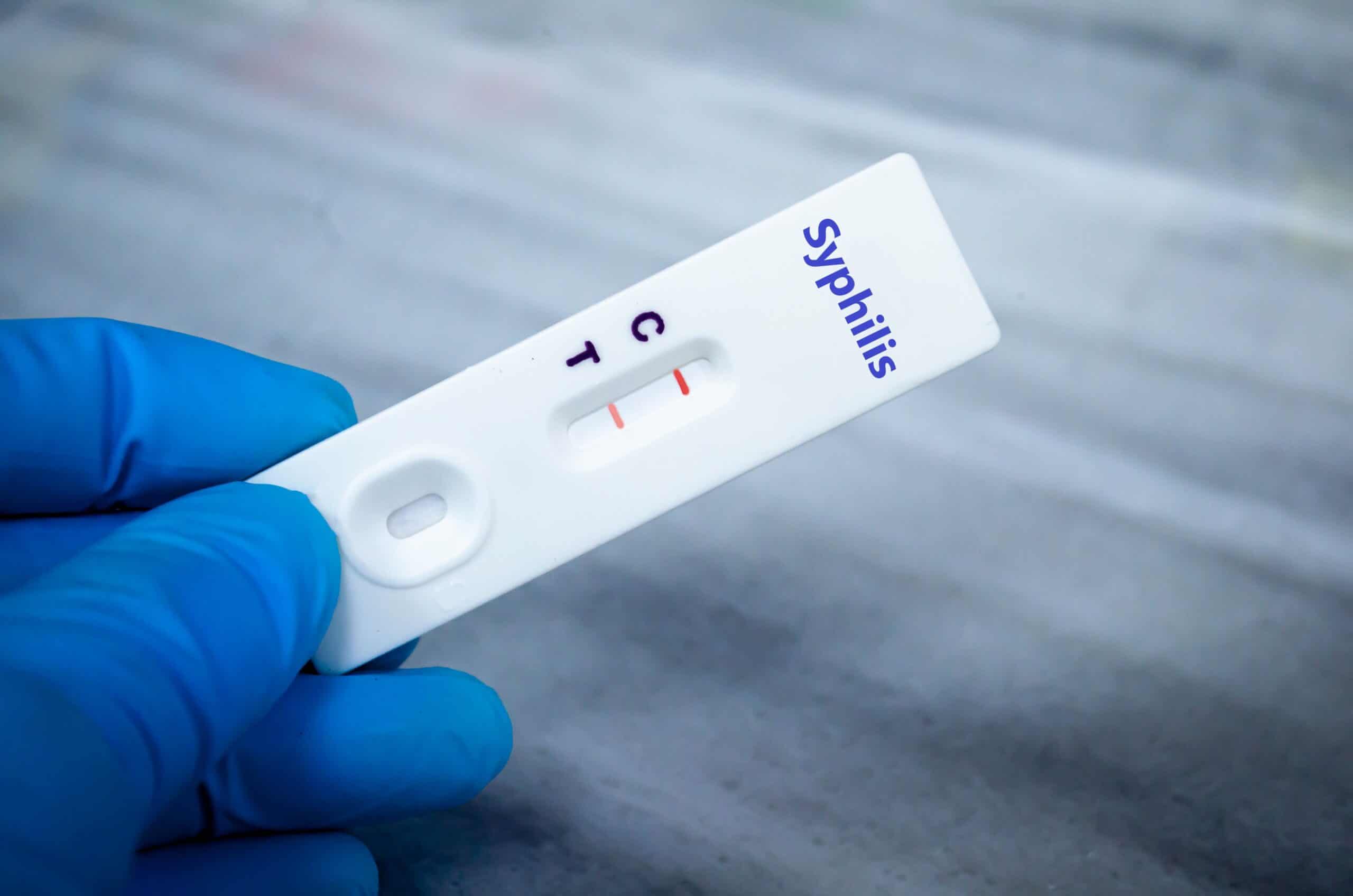
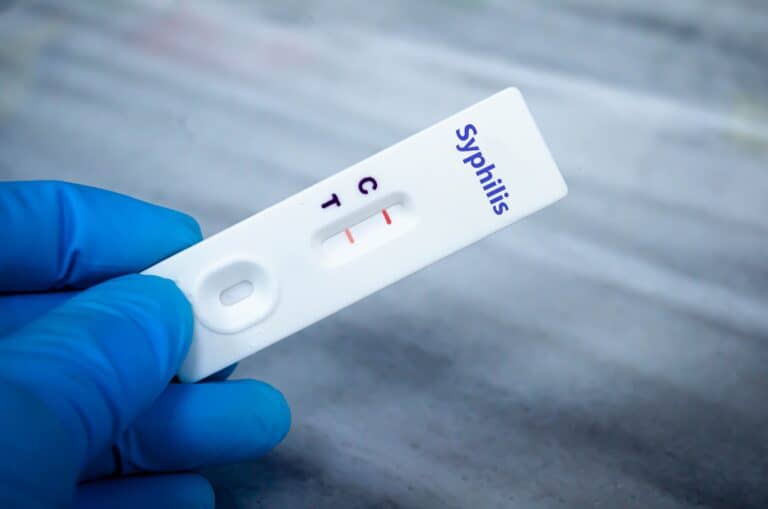
Syphilis Diagnosis
Syphilis can be asymptomatic in some individuals, making diagnosis essential for those at risk. Blood tests are commonly used:
- VDRL (Venereal Disease Research Laboratory) Test: A preliminary screening to detect antibodies. A negative result indicates no infection, while a positive result requires confirmation.
- TPPA (Treponema Pallidum Particle Agglutination): A more precise test to confirm syphilis infection.
How Long Does Syphilis Treatment Take?
Treating syphilis in its early stages is relatively quick and effective. Doctors typically prescribe penicillin antibiotics and closely monitor the patient’s progress. Abstaining from sexual activity until fully cured is essential to prevent transmission and reinfection. Untreated or improperly managed syphilis can prolong the treatment period and reduce its effectiveness.
Prevention and Risk Reduction
Preventing syphilis is straightforward with these measures:
- Always use condoms during sexual activity.
- Avoid frequent partner changes to reduce the risk of STDs.
- Have regular health check-ups, especially for individuals at risk.
- Pregnant women should undergo syphilis screening and treatment to prevent mother-to-child transmission.
Frequently Asked Questions About Syphilis
Can Syphilis Be Completely Cured?
Yes, if detected and treated early, syphilis is completely curable with no long-term effects.
Can Untreated Syphilis Be Fatal?
Yes, if syphilis progresses to the tertiary stage, it can severely affect the heart, brain, and other vital organs, leading to death.
How Do Symptoms Differ Between Men and Women?
In the primary stage, symptoms vary based on the location of the sores. In women, sores may appear on the genitals, accompanied by white patches on the tongue and vaginal discharge. In men, sores typically form on the penis, scrotum, groin, or anus. In the secondary and tertiary stages, symptoms are generally the same for both sexes.
Get Tested for Syphilis at ReadyCheckGo Before Complications Arise
If you’ve had unprotected sex or suspect your partner may be infected, get tested for syphilis promptly, even if you have no symptoms. Early syphilis treatment and detection can prevent severe complications and future transmission. Book an appointment with ReadyCheckGo today. Testing is available anonymously at our Silom, Thonglor, and Samui locations or via home visits in Bangkok and nearby provinces.
References:
- “Syphilis Awareness and Prevention,” retrieved on December 12, 2024, from https://www.siphhospital.com/th/news/article/share/syphilis
- “Syphilis,” retrieved on December 12, 2024, from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/syphilis
simple & private under medical standard
Express STDs
test & treat in Bangkok
No need to go to hospital, you can get
Then, receive your online results!
Prioritize privacy with our anonymous STD testing service.
Open to all with enthusiastic staff catering to diverse genders and ethnicities.
Silom branch
Near BTS Chong-nontri
Sukhumvit branch
BTS Thong-lo (Exit 3)
บทความที่น่าสนใจ
Syphilis: Treat It Early to Avoid Vital Complications
Had unprotected sex or condom failure? Get PEP, the emergency HIV prevention medication, within 72 hours to reduce the risk of HIV infection.
Steps for Getting PEP Medication After HIV Risk Exposure
Had unprotected sex or condom failure? Get PEP, the emergency HIV prevention medication, within 72 hours to reduce the risk of HIV infection.
What is an HPV Infection?
HPV infections are a major health concern for Thai women, with some strains leading to cervical cancer. Discover the key prevention and treatment methods.
What is Herpes? Causes, Prevention, and Treatment
Herpes Simplex is a common STI affecting skin and mucous membranes. HSV-1 typically affects the mouth, while HSV-2 usually impacts the genital area.
What Is Gonorrhea And Why It’s Crucial To Treat It Early
Gonorrhea, left untreated, can cause infertility and severe complications. Schedule a consultation to prevent further health issues.
The Difference Between HIV and AIDS
While often used interchangeably, HIV and AIDS are not the same. Learn how they differ, how HIV is transmitted, and important prevention tips.